Configure Common Pre-requisites¶
GitOps Authentication¶
For synchronizing the Git repo with the cluster, Hyperledger Bevel configures Flux for each cluster. The authentication is via SSH or HTTPS which can be specified in the configuration file gitops.protocol section.
For HTTPS, just generate a git token and give that read-write access. Keep the token safe and use in the gitops.password section of the configuration file.
For SSH, run the following command to generate a private-public key pair named gitops.
ssh-keygen -q -N "" -f ./gitops
The above command generates an SSH key-pair: gitops (private key) and gitops.pub (public key).
Use the path to the private key (gitops) in the gitops.private_key section of the configuration file.
NOTE: Ensure that the Ansible host has read-access to the private key file (gitops).
And add the public key contents (starts with ssh-rsa) as an Access Key (with read-write permissions) in your Github repository by following this guide.
Unseal Hashicorp Vault¶
The Hashicorp Vault service should be accessible by the ansible controller as well as the kubernetes cluster (proper inbound/outbound rules should be configured). If not initialised and unsealed already, complete the following steps to unseal and access the Vault.
- Install Vault client. Follow the instructions on Install Vault.
- Set the environment Variable VAULT_ADDR as the Vault service.
export VAULT_ADDR=http://my-vault-server:9000
NOTE The port should be accessible from the host where you are running this command from, as well as the Ansible controller and the Kubernetes nodes.
- Now execute the following:
vault operator init -key-shares=1 -key-threshold=1
It will give following output:
Unseal Key 1: << unseal key>>
Initial Root Token: << root token>>
Save the root token and unseal key in a secure location. This root token is to be updated in Hyperledger Bevel’s network.yaml file before running the Ansible playbook(s) to deploy the DLT/Blockchain network.
- Unseal with the following command:
vault operator unseal << unseal-key-from-above >>
- Run this command to check if Vault is unsealed:
vault status
NOTE: It is recommended to use Vault auto-unseal using Cloud KMS for Production Systems. And also, rotate the root token regularly.
Docker Images¶
Hyperledger Bevel provides pre-built docker images which are available on GitHub Repo. Ensure that the versions/tags you need are available. If not, raise it on our Discord Channel.
For Corda Enterprise, the docker images should be built and put in a private docker registry. Please follow these instructions to build docker images for Corda Enterprise.
NOTE: Hyperledger Bevel recommends use of private docker registry for production use. The username/password for the docker registry can be provided in a network.yaml file so that the Kubernetes cluster can access the registry.
DNS Update¶
Hyperledger Bevel uses Ambassador or HAProxy Ingress Controller (for Fabric) for inter-cluster communication.
Bevel automation deploys both as per the configuration provided in network.env.proxy section of the Bevel configuration file, but if you are not using External DNS, you will have to manually add DNS entries.
After Ambassador/HAProxy is deployed on the cluster (manually or using
platforms/shared/configuration/kubernetes-env-setup.yamlplaybook), get the external IP address of the Ambassador/HAProxy service.kubectl get services -o wide
The output of the above command will look like this:
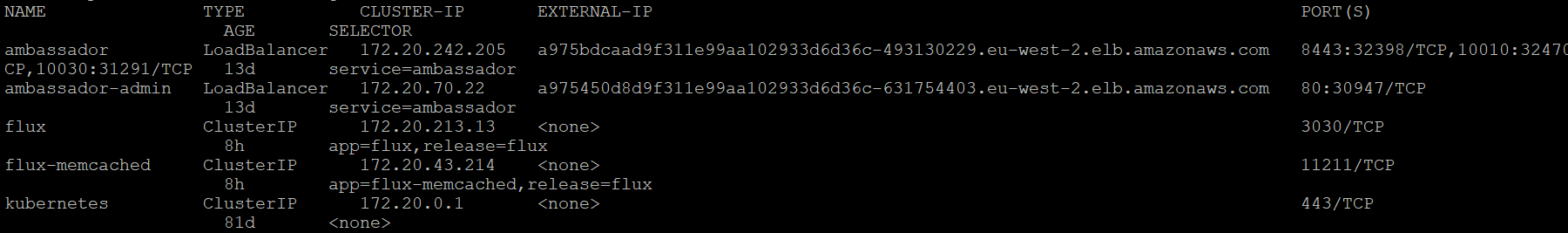 Ambassador Service Output
Ambassador Service OutputCopy the EXTERNAL-IP for ambassador service from the output.
NOTE: If Ambassador is configured by the playbook, then this configuration has to be done while the playbook is being executed, otherwise the deployment will fail.
- Configure your subdomain configuration to redirect the external DNS name to this external IP. For example, if you want to configure the external domain suffix as test.corda.blockchaincloudpoc.com, then update the DNS mapping to redirect all requests to *.test.corda.blockchaincloudpoc.com towards EXTERNAL-IP from above as an ALIAS.
In AWS Route53, the settings look like below (in Hosted Zones).
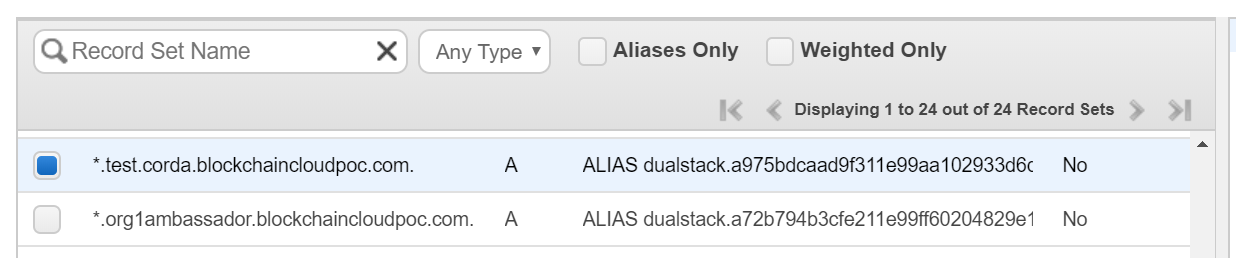 Ambassador DNS Configuration
Ambassador DNS Configuration
NOTE: Ambassador for AWS and AWS-baremetal expose Hyperledger Indy nodes via a TCP Network Load Balancer with a fixed IP address. The fixed IP address is used as EIP allocation ID for all steward public IPs found in the network.yaml. The same public IP is specified for all stewards within one organization. All ports used by Indy nodes in the particular organization have to be exposed.
External DNS¶
In case you do not want to manually update the route configurations every time you change DNS name, you can use External DNS for automatic updation of DNS routes.
Follow the steps as per your cloud provider, and then use external_dns: enabled in the env section of the Bevel configuration file (network.yaml).
NOTE: Detailed configuration for External DNS setup is not provided here, please refer the link above.